Weekly Advanced Technologies〔95〕

Weekly Advanced Technologies〔95〕 | Novel Approach Resolves Challenges in Plant Single-Cell Sequencing; Optogenetic Metabolic Flux Regulation in Yeast via a Blue-Light Switch
To address the difficulty of sample preparation in plant single-cell sequencing, a research team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed the FX-Cell series of new technologies, significantly improving efficiency and data quality.
Researchers have developed the optogenetic tool OptoPdc1, which precisely and reversibly regulates glycolysis and product synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through blue light, providing a new paradigm for metabolic engineering.
Based on the weekly diary of technology provided by the daily list of the NCSTI online service platform, we launch the column "Weekly Advanced Technologies" at the hotlist of sci-tech innovation. Today, let's check out No.95.
1. Nature Methods丨Novel Approach Resolves Challenges in Plant Single-Cell Sequencing
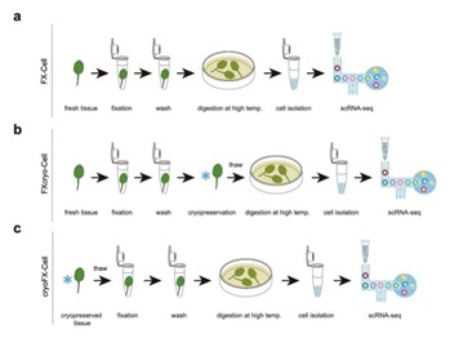
FX-Cell and Its Derivative Technology Workflows
High-throughput single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is limited by technical bottlenecks in single-cell preparation in plant and agricultural research. Through underlying technological innovation, the Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and other institutions have developed a novel plant single-cell preparation method called FX-Cell.
This method improves the traditional protoplast preparation process: the research team first discovered that increasing the enzymatic hydrolysis temperature can enhance efficiency. However, to avoid transcriptome disturbance caused by high temperatures, tissues are fixed with Farmer's solution before enzymatic hydrolysis. Meanwhile, GMP Sepharose/Agarose column affinity purification is used to remove RNase from the enzymatic hydrolysis solution, and RNase inhibitors such as tRNA and tri-GMP are added to the system to effectively protect mRNA stability, thereby increasing the number of single-cell gene captures. In tests on rice and Arabidopsis root tips, FX-Cell showed high reproducibility, with data quality comparable to conventional scRNA-seq, superior to snRNA-seq, and basically eliminating transcriptome bias caused by protoplastization. Based on this, the team further developed two derivative technologies: FXcryo-Cell (fixation first, then -80°C preservation followed by enzymatic hydrolysis) and cryoFX-Cell (cryopreservation first, then fixation and enzymatic hydrolysis). Taking rice root tips as an example, the quality of single-cell atlases obtained by both is comparable to that of FX-Cell.
These technologies enable high-quality scRNA-seq of hard-to-digest tissues, field-collected samples, and cryopreserved samples, providing important tools for constructing plant single-cell atlases and advancing precise agricultural research.
2. ACS Synthetic Biology丨Optogenetic Metabolic Flux Regulation in Yeast via a Blue-Light Switch
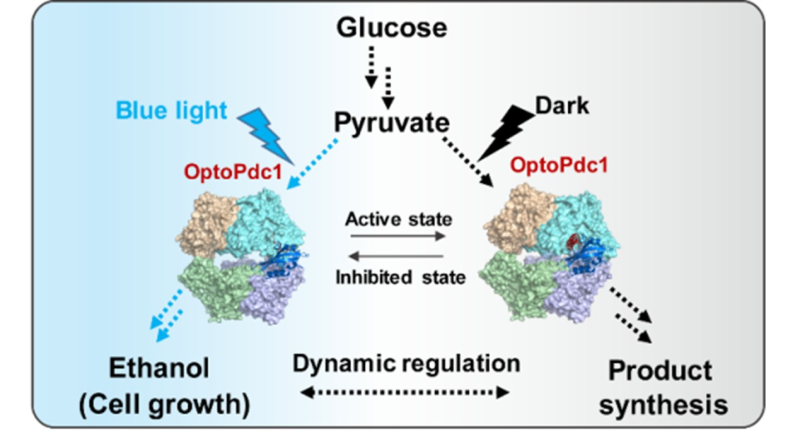
Schematic Diagram of the Light-Controlled Metabolic Regulation System in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
A research team from the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has made significant progress in the dynamic regulation of metabolic flux in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Targeting pyruvate decarboxylase Pdc1, a key enzyme in glycolysis, the team developed the optogenetic regulation tool OptoPdc1 at the protein level. By introducing a blue light-responsive domain and constructing a variety of photosensitive mutants, OptoPdc1 can directly, rapidly, and reversibly regulate the catalytic activity of Pdc1 under the switch between blue light and darkness. Based on this, the team constructed the light-controlled Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain Opto-S. cerevisiae, realizing efficient dynamic regulation of cell growth and ethanol synthesis: under blue light irradiation, the ethanol production regulation range reaches 120-fold, which is positively correlated with light intensity. The system has simple components, rapid response, and reversible regulation. It supports efficient cell biomass accumulation under dark conditions, while blue light irradiation inhibits ethanol production, creating a favorable environment for synthetic pathways dependent on respiratory metabolism. The team further applied this system to isobutanol synthesis, achieving responsive regulation of isobutanol titer through different blue light pulse modes. The yield of the light-controlled strain can reach 120% of that of the non-light-controlled strain.
This research not only provides a new protein-level regulation strategy for Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolic engineering but also opens up an innovative path for the dynamic and precise biosynthesis of high-value chemicals.
3. IEEE JSSC丨Dual-Edge Ping-Pong Architecture Improves Millimeter-Wave Clock Performance
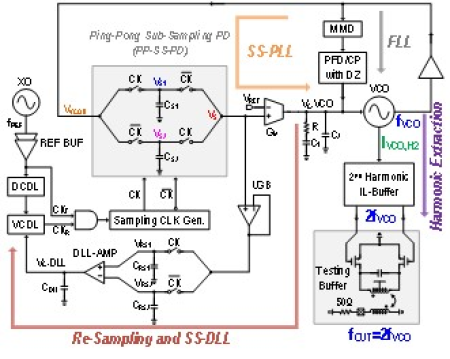
Circuit Structure of the Ping-Pong Sub-Sampling Phase-Locked Loop
Focusing on 5.5G/6G wireless communications and next-generation high-speed serial interfaces, and addressing the stringent requirement for ultra-low jitter of millimeter-wave local oscillator clocks, the Institute of Microelectronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Tsinghua University have achieved important breakthroughs in sub-sampling phase-locked loop (SSPLL) technology through cooperation.
Although traditional SSPLL has the advantage of high phase detection gain, there is a difficult design trade-off between loop bandwidth, in-band phase noise, and reference spurs. To this end, the team innovatively proposed a "dual-edge ping-pong sub-sampling phase-locked loop" architecture. By simultaneously utilizing the rising and falling edges of the reference clock, it realizes equivalent reference frequency multiplication, effectively alleviating the above contradictions and significantly improving loop performance. In addition, the team developed a high-power and area-efficient injection-locked buffer, which can efficiently extract the second harmonic of the voltage-controlled oscillator while performing harmonic shaping to further suppress out-of-band phase noise. Based on these two core technologies, the research team developed a K-band phase-locked loop clock chip using 65nm CMOS process, with an output frequency range of 22.4–25.6 GHz, an overall power consumption of less than 18 mW, an RMS integrated jitter of better than 50 fs, and a jitter-power figure of merit (FoM) of below −254 dB.
This achievement provides a high-performance and low-power clock solution for future 6G communications, terahertz systems, and ultra-high-speed data interfaces.
4. Advanced Science丨AI-Powered Multitasking Platform Boosts High-Throughput Enzyme Screening
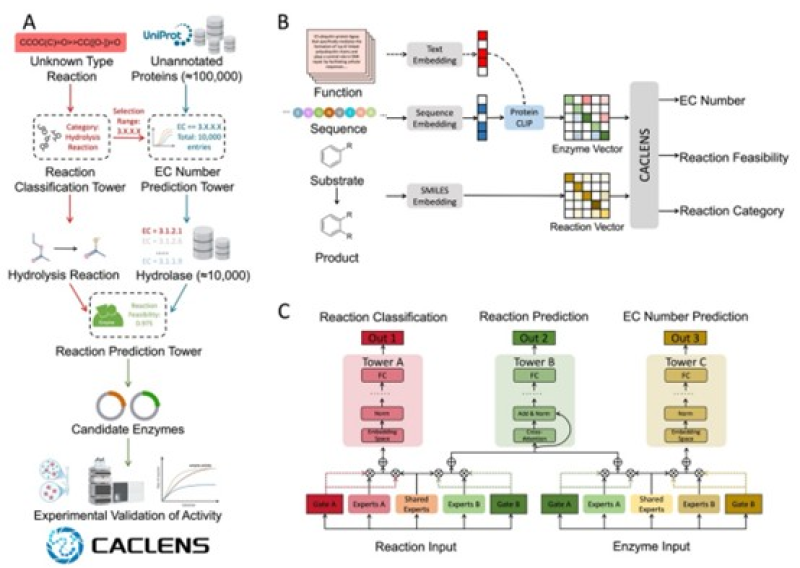
Intelligent Mining and Screening Framework for New Functional Enzymes Based on Multi-Task Models
To address the challenge of efficient screening of functional enzymes, the Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has constructed an end-to-end, multi-task computational framework called Cross-Attention & Contrastive Learning-enabled Enzyme Selection (CACLENS).
Existing deep learning methods lack the ability to uniformly model multi-modal inputs and multi-task outputs, making it difficult to meet the demand for high-performance enzyme mining. CACLENS innovatively integrates CGC gating mechanism, contrastive learning, and cross-attention technology to realize integrated prediction of three key tasks: reaction type classification, EC number prediction, and reaction feasibility evaluation. The framework outperforms existing models in multiple indicators: after removing interference from common cofactors such as ADP/ATP/H⁺, reaction type classification is more accurate; the overall performance of EC number prediction surpasses the mainstream model CLEAN; in reaction feasibility evaluation, it still performs better even when adopting strategies biased towards ESP or EnzRank, and has strong generalization ability for low-similarity or unseen sequences. The research team applied CACLENS to the mining of zearalenone (ZEN)-degrading enzymes, screening 10 candidate enzymes from a large-scale sequence space. After gene synthesis, heterologous expression, and in vitro verification, 5 of them showed ZEN-degrading activity, with the degradation efficiency of ZD4 and ZD7 exceeding 90%.
This work demonstrates the practical value of CACLENS in functional enzyme discovery, providing key technical support for the construction of intelligent enzyme engineering platforms and the development of new enzymes for mycotoxin biodegradation.